
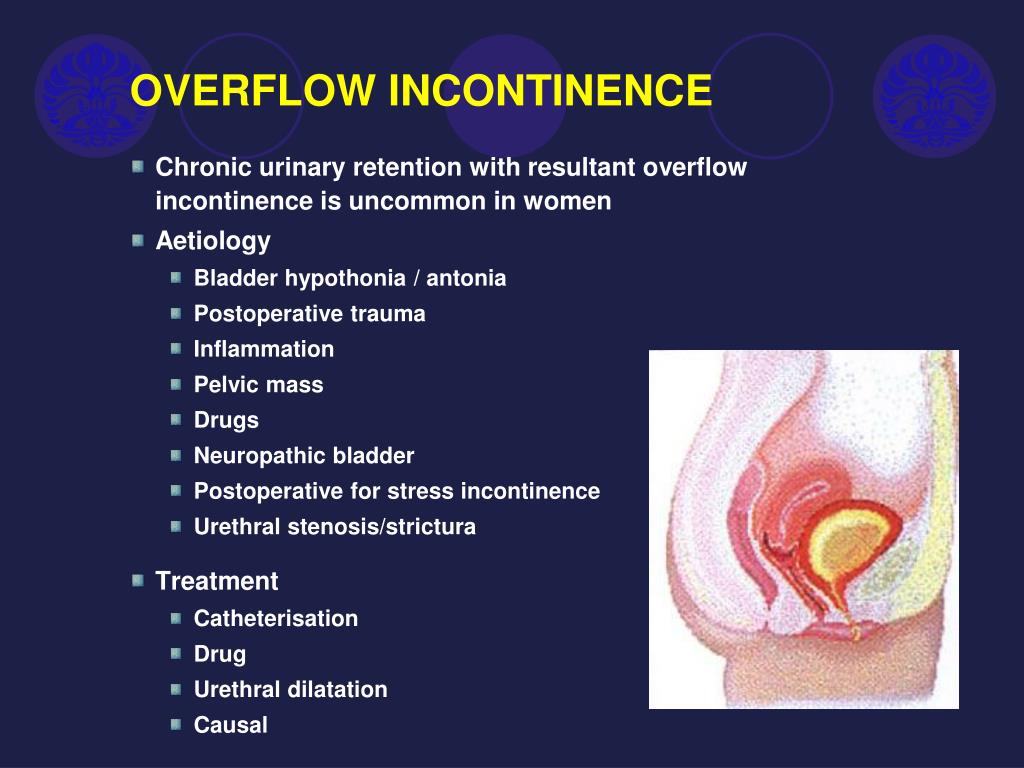
The prevalence of UI is higher in women than in men 80 years of age or younger, but both men and women are affected almost equally after age 80. In 2007, it was estimated that more than 25 million people in the U.S. have UI, which is associated with significant morbidity and decreased quality of life. 1Īpproximately 10 million patients in the U.S. OAB comprises a constellation of symptoms typically characterized by urgency, with or without UUI, accompanied by frequency and nocturia. The term overactive bladder (OAB) is often used to describe UI. OFI may result in LUTS and in the loss of small amounts of urine it most often occurs in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Overflow incontinence (OFI) is caused by a hypotonic bladder, bladder outlet obstruction, or other forms of urinary retention. Mixed urinary incontinence (MUI) includes features of both UUI and SUI. Stress urinary incontinence (SUI) is defined as involuntary urine leakage associated with specific activities (e.g., sneezing and coughing. Urge urinary incontinence (UUI) is defined as involuntary urine leakage associated with urgency. UI can be further defined by the patient’s presentations and symptoms. UI is characterized by lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), which include both storage and voiding problems. Urinary incontinence (UI) may be defined as any involuntary or abnormal urine loss.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
